Antimicrobial stewardship programme
How did antibiotic resistance become a problem?
When use appropriate antibiotic saves lives and help your body fight infections by killing bacteria, however some bacteria escape the medication and become resistance to the antibiotics, these bacteria increase and cause the person to get sick again.
When this happens, different antibiotics needed to kill the bacteria increasing the chance of even more bacteria becoming resistance making you sick longer requiring an additional medication and cost.
Additional antibiotics could lead to serious side effects viz
1. Allergic reactions
2. Harm to other organs
3. Nausea
4. Harm to kidney
5. Vomiting
6. Diarrhoea
What can be done to slow down the antibiotic resistance?
We must promote the use of antibiotics only when they can help and only when the antibiotics are necessary.
We must remember that, more we use antibiotics more likely resistance bacteria will develop and spread.
Do not take an antibiotic for a virus such as cold and flu.
What is C diff Infection?
C diff is also called Clostridium defficile Toxin. C diff infection was the side effect of taking antibiotic and could have been severe or life-threatening if untreated.
This infection develop because the antibiotics killed much of our normal bacteria leaving space for more dangerous bacteria to take over.
How to slow down antibiotic resistance?
In hospital doctors frequently prescribed antibiotics for UTI, however many UTI are misdiagnosed.
If urine culture shows bacteria a common practices has been to give an antibiotics.
However, we know that in older people sometimes bacteria can be in the bladder without causing an infection or harm.
For that reason, a positive urine culture in a person without any symptoms, should not treated with antibiotic and before giving antibiotics accesses the patient for infection sign or symptoms. If none of present take steps to monitor the patient and make sure he is feeling well and do not develop new symptoms.
What is stewardship?
“The careful and responsible management of something entrusted to one‘s care”.
Tools for optimizing antimicrobial use, termed as “antimicrobial stewardship”.
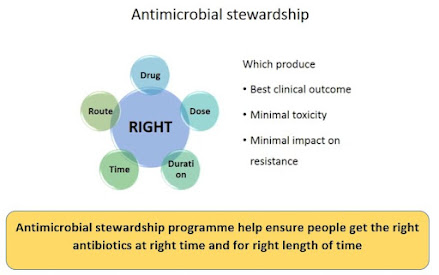
What is Antimicrobial stewardship programme?
“Coordinated interventions designed to improve and measure the appropriate use of antimicrobial agents by promoting the selection of the optimal antimicrobial drug regimen including Dosing, duration of therapy, and route of administration”.
In other words
Antimicrobial stewardship is a coordinated program that promotes the appropriate use of antimicrobial agents, improve patient outcomes, reduce microbial resistance, and decreases the spread of infections caused by multidrug resistant organisms.
Antibiotic stewardship programme is judicious use of antibiotics so that in order to avoid the emergence of resistance and patient are getting appropriate treatment for required period.
Stewardship program stress chossing the right dosages, for the right duration. Antimicrobial stewardship is not just antibacterial drug but antivirals, antifungals and antiparastic agents.
Goal of Antimicrobial Stewardship program
· To optimize safe and appropriate use of AMA to improve clinical outcomes while minimizing unintended consequence of antimicrobial use.
· To reduce Antimicrobial resistance
· To reduce healthcare cost
· To reduce antibiotic induced collateral damage
The Goal of stewardship program, is to create an environment where improvement intervention will be most successful.
Antimicrobial stewardship programme TEAM
It shall be multidisciplinary team
1. Infectious disease clinician
2. Pharmacologist
3. Clinical microbiologist
4. Infection control nurse
5. Administrator
Core Elements of Antimicrobial stewardship programme
1. Leadership Commitment: Dedicate necessary human, financial, and information technology resources.
2. Accountability: Appoint a leader or co leader such as a physician and pharmacist, responsible for program management and outcomes.
3. Drug expertise: Appoint a pharmacist ideally as the co leader of the stewardship program, to help lead implementation efforts to improve antibiotic use.
4. Action: Implement interventions, such as prospective audit and feedback or preauthorization, to improve antibiotic use.
5. Tracking: Monitor antibiotic prescribing, impact of interventions and other important outcomes, like C difficile infection and resistance patterns.
6. Reporting: Regularly report information on antibiotic use and resistance to prescribers, pharmacist, nurses and hospital leadership.
7. Education: Educate prescriber’s, pharmacist nurses and patients about adverse reaction from antibiotics, antibiotic resistance and optimal prescribing.
Essential steps of Antimicrobial stewardship programme
Prospective audit with intervention and feedback
1. Identify the current resistance patterns
2. Give feedback to clinicians
3. Improve antibiotics use by optimizing
a. Drug selection
b. Dose
c. Duration
d. Route
Formulary restrictions/preauthorization
· ASP team identify Antimicrobial Agents which require prior authorization
o Limit the use of selected AMAs for specific indication
· Review of the antibiotic order for
o Continue or discontinue AMA
o Change or adjust the AMA
Switch from parental to oral therapy
· Serious infection: hospitalization with parenteral therapy
· Bioavailability of certain AMA enhanced by oral route
· Patient meets defined clinical criteria
· Allows conversion to oral therapy
Streaming/De-escalation
· Broad-spectrum therapy- selection resistant pathogen
Culture reports to promote de-escalating empiric therapy to targeted therapy
· Review of antibiotics in 48hours after prescription
o Response?
o Dose, duration, route?
o Is de-escalation possible?
Appropriate use of microbiology lab
· Microbiology laboratory
o Identification of microbial pathogens
o Performance of susceptibility testing
· Actively involved in resistance surveillance
· Local antibiogram should be updated
Education
· Education- Essential element for prescribing behavior
· Educational activities- lecture or informational pamphlets
· ASP provide regular update on
o Antibiotic prescribing
o Antibiotic resistance
o Infectious Disease management.
Methodology
· Clinical pharmacist driven Antibiotic stewardship Program
· ASP team
· All patient on high end antibiotics are reviewed
· Recommendation are given
· Follow up on compliance takes place
Audit: Monitoring compliance
· Are Antibiotics being used in accordance with approved protocols
o Empirical Vs targeted treatment clearly specified
o Stopped at the correct time
o Based on clinical needs and microbiology results
o Correct use of surgical prophylaxis guidelines
o Antibiotic
o Timing
o Dosage





Post a Comment